The last few weeks have given us the opportunity to do some camping in and around LA, namely Monte Cristo in the Angeles Forest and a trip to Joshua Tree.
Angeles Forest – Monte Cristo
Our first weekend we headed out to the Angeles Forest and spent a night at the Monte Cristo campsite. Campsites are all first come first serve. We got there midday on Saturday and about half the campsites were still available, but by the time sunset came around, the campground was pretty much full.
There’re no rangers at the campsite, so you buy yourself a permit at the entrance, and drop money in the drop-box. There are no ablution facilities besides a couple longdrop toilets which were surprisingly clean. Each site is quite large and has parking for two vehicles. Even though all the sites were full, there’s enough space that you don’t feel people are on top of you. Drinking water taps are shared between adjoining campsites. The campsite is nestled nicely in one of the valleys with a river running through it. It is right next to the road, but traffic isn’t that heavy. While the Angeles Forest has plenty of hiking opportunities, none are close enough to the campsite to hike from there. You’ll have to drive to a trailhead before starting a hike.
The campsite is nestled nicely in one of the valleys with a river running through it. It is right next to the road, but traffic isn’t that heavy. While the Angeles Forest has plenty of hiking opportunities, none are close enough to the campsite to hike from there. You’ll have to drive to a trailhead before starting a hike.
It was nice to be able to quickly get out of the city and just relax with nothing going on. We didn’t get any cell reception at the campsite itself, adding to the quietness. Angeles Forest has a lot of other campsites which we’re keen to checkout, especially with summer on its way, opening up some of the campsites which were inaccessible during the winter.
Joshua Tree – Joshua Tree Lake
The next week, we headed out early on Friday and drove out to Joshua Tree. Joshua Tree has a mix of reservation and first come, first serve campgrounds. The reservations were full weeks before, and only arriving late on Friday afternoon, we decided to play it safe and camped just outside Joshua Tree at a private campground, Joshua Tree Lake. The campsite is quite close to the West Entrance Station of Joshua Tree, which never closes, so you can head into the park whenever it suits you. Joshua Tree Lake has a mixture of campsites and RV spots. The campsites aren’t demarcated, so you just find a spot where there’s space. It wasn’t particularly busy so we chose a spot without anyone nearby. Barrel fires and camping tables are provided, although if it gets very busy, I doubt there’re enough for everyone.
The campsite is quite close to the West Entrance Station of Joshua Tree, which never closes, so you can head into the park whenever it suits you. Joshua Tree Lake has a mixture of campsites and RV spots. The campsites aren’t demarcated, so you just find a spot where there’s space. It wasn’t particularly busy so we chose a spot without anyone nearby. Barrel fires and camping tables are provided, although if it gets very busy, I doubt there’re enough for everyone.
Being in a dessert environment, there’s no grass for camping, but even with a howling wind the whole time, dust was not an issue. Ablutions were clean and showers are also provided.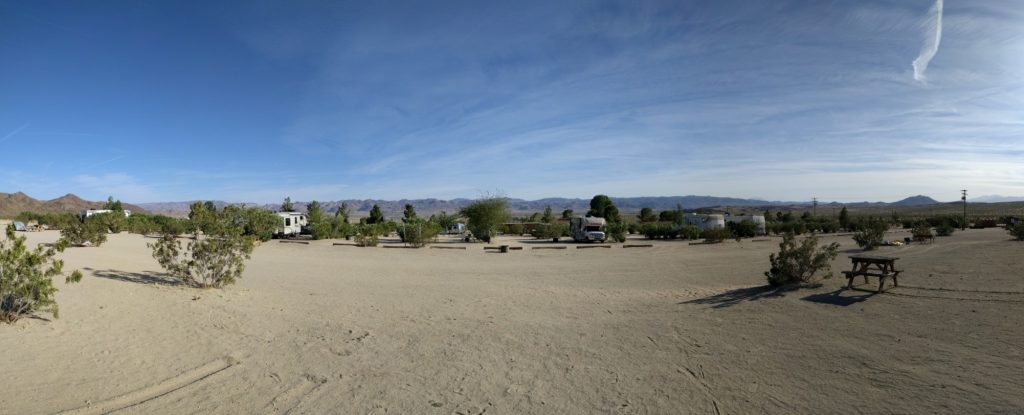 We spent Saturday in the north end of the park, hiking Ryan Mountain and Lost Horse Mine. All the trailheads have limited parking, and in the busy spring, you’re not guaranteed a spot. We were lucky though, arriving early enough at Ryan Mountain that there were open spaces, and getting lucky at Lost Horse Mine that we arrived as another vehicle was leaving.
We spent Saturday in the north end of the park, hiking Ryan Mountain and Lost Horse Mine. All the trailheads have limited parking, and in the busy spring, you’re not guaranteed a spot. We were lucky though, arriving early enough at Ryan Mountain that there were open spaces, and getting lucky at Lost Horse Mine that we arrived as another vehicle was leaving.
Neither hike was particularly difficult. Ryan Mountain is a straight up, straight back down route that is quite popular and offers good views from a central location. Lost Horse Mine was a flatter and longer loop. It goes past an old gold mine, and some of the buildings still remain there for you to see.
Before heading back to our campsite we decided to drive out to Keys View. It’s well worth it, with spectacular views into the Coachella Valley, spanning as far as the Salton Sea. We considered doing a section of the Geology Tour Road, but it’s marked 4×4 only, and although some of it is supposedly accessible to two wheel drive vehicles, we didn’t feel like risking getting stuck in the sand.
On Sunday we drove all the way through the park towards Cottonwood Springs. It was pretty amazing seeing the vegetation change from the Joshua Tree packed Mojave Desert in the North, to the Colorado Desert in the South. We did a short hike up to Mastodon Peak, which again offered good views.
While we knew Joshua Tree was popular, we didn’t have major expectations, which resulted in an amazing trip. I don’t know if it was just the recent rains, but the park offers stunning scenery with many hikes and other points of interest to keep you busy. We stopped off at Hidden Valley to watch some of the rock climbers do their thing too at some of the world famous routes too.
California has camp grounds everywhere you look, so we’re looking forward to doing some more exploring in the future.